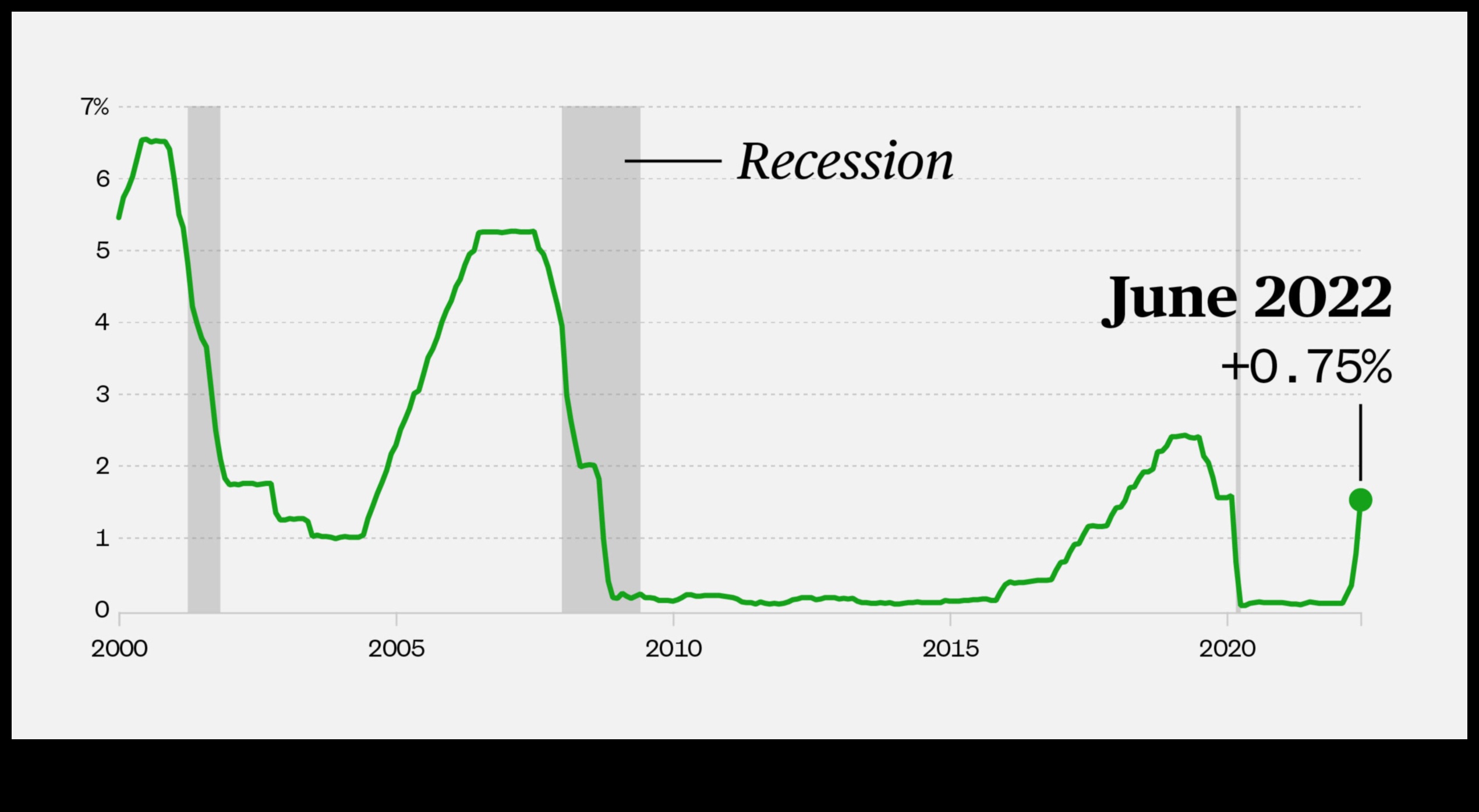
What is the federal funds rate?
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is one of the most important tools that the Federal Reserve uses to control the money supply and inflation.
When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can slow down economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can stimulate economic growth.
People who search for “what is the federal funds rate” are likely trying to understand how the Fed’s monetary policy is affecting the economy and how it might affect their own finances. They may also be looking for information on how to invest in the stock market or other financial instruments.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Federal Funds Rate | The interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans |
| Interest Rate | The cost of borrowing money |
| Monetary Policy | The actions taken by a central bank to influence the economy |
| Federal Reserve | The central bank of the United States |
| Central Bank | An institution that regulates the money supply and interest rates |
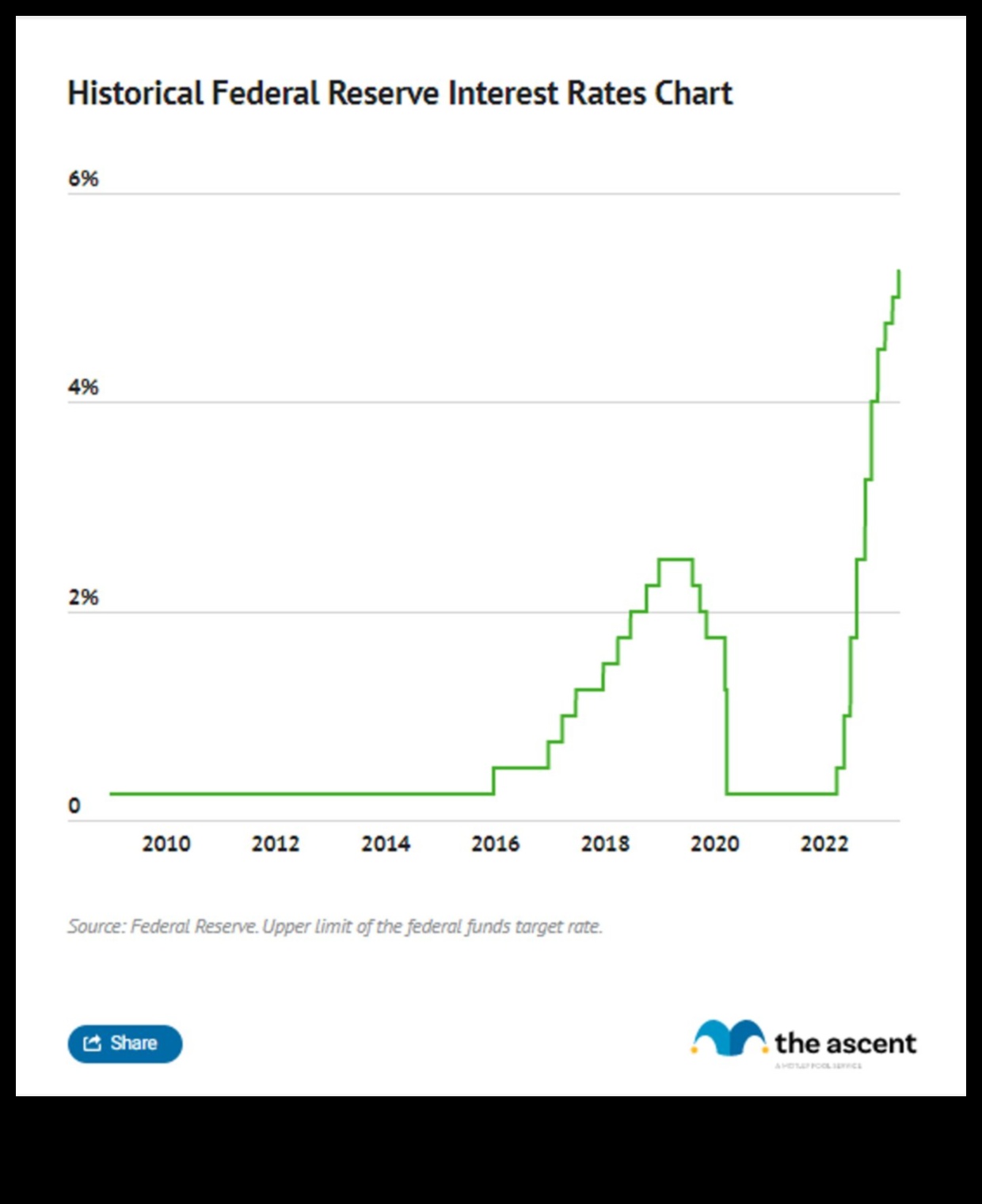
II. How is the Federal Funds Rate set?
The federal funds rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is the monetary policy-setting arm of the Federal Reserve. The FOMC meets eight times per year to review the economic outlook and make decisions about whether to raise, lower, or leave the federal funds rate unchanged. The FOMC’s decisions are based on a number of factors, including inflation, economic growth, and employment.
When the FOMC decides to raise the federal funds rate, it does so by selling Treasury securities in the open market. This increases the supply of money in the banking system, which in turn raises the demand for federal funds. This causes the federal funds rate to rise.
When the FOMC decides to lower the federal funds rate, it does so by buying Treasury securities in the open market. This reduces the supply of money in the banking system, which in turn reduces the demand for federal funds. This causes the federal funds rate to fall.
The federal funds rate is a powerful tool that the Fed can use to influence the economy. By raising or lowering the federal funds rate, the Fed can affect the cost of borrowing money, which in turn affects economic growth, inflation, and employment.
III. What is the target federal funds rate?
The target federal funds rate is the interest rate that the Federal Reserve aims to achieve through its monetary policy actions. The Fed uses a variety of tools to influence the federal funds rate, including open market operations, discount window lending, and reserve requirements. The target federal funds rate is an important tool for the Fed to control the money supply and inflation. When the Fed raises the target federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can slow down economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the target federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can stimulate economic growth.
The target federal funds rate is not a fixed number. It is constantly being adjusted by the Fed in response to changes in economic conditions. The Fed typically announces changes to the target federal funds rate at its regularly scheduled meetings.
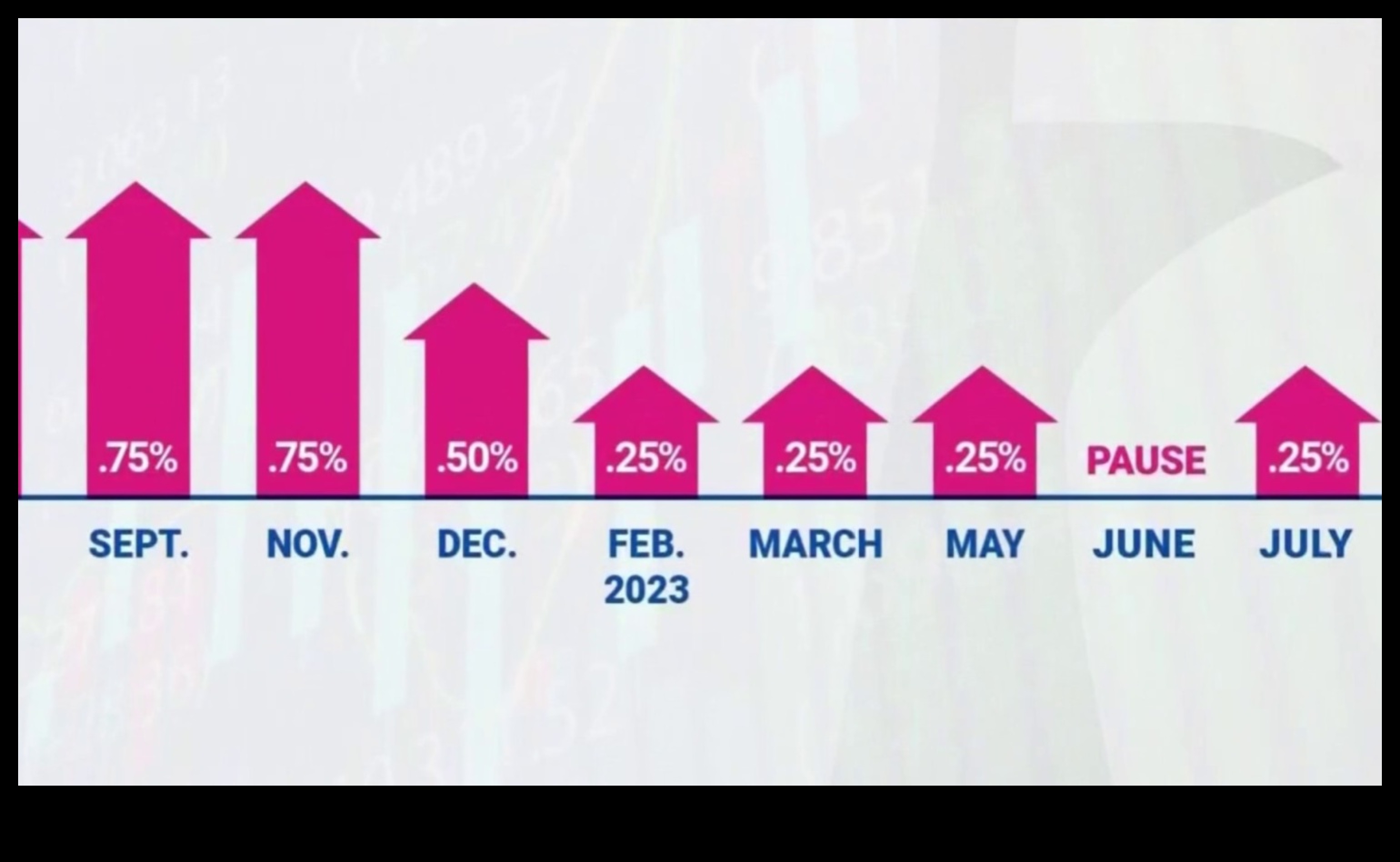
IV. What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and the economy?
The federal funds rate is a key determinant of the overall level of interest rates in the economy. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can slow down economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can stimulate economic growth.
The federal funds rate also affects the exchange rate between the dollar and other currencies. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes the dollar more attractive to investors, which can cause the value of the dollar to increase. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes the dollar less attractive to investors, which can cause the value of the dollar to decrease.
The federal funds rate is also used to target inflation. When the Fed wants to reduce inflation, it raises the federal funds rate. This makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which in turn reduces the amount of money that is available in the economy. This can slow down economic growth and reduce inflation. Conversely, when the Fed wants to increase inflation, it lowers the federal funds rate. This makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which in turn increases the amount of money that is available in the economy. This can stimulate economic growth and increase inflation.
The federal funds rate is a powerful tool that the Fed can use to influence the economy. However, it is important to note that the Fed’s decisions about the federal funds rate can have unintended consequences. For example, raising the federal funds rate can slow down economic growth more than the Fed intended, or lowering the federal funds rate can increase inflation more than the Fed intended.
The Fed carefully monitors the economy and uses a variety of factors to make decisions about the federal funds rate. These factors include the unemployment rate, inflation, economic growth, and the housing market. The Fed also takes into account the opinions of economists and other experts when making decisions about the federal funds rate.
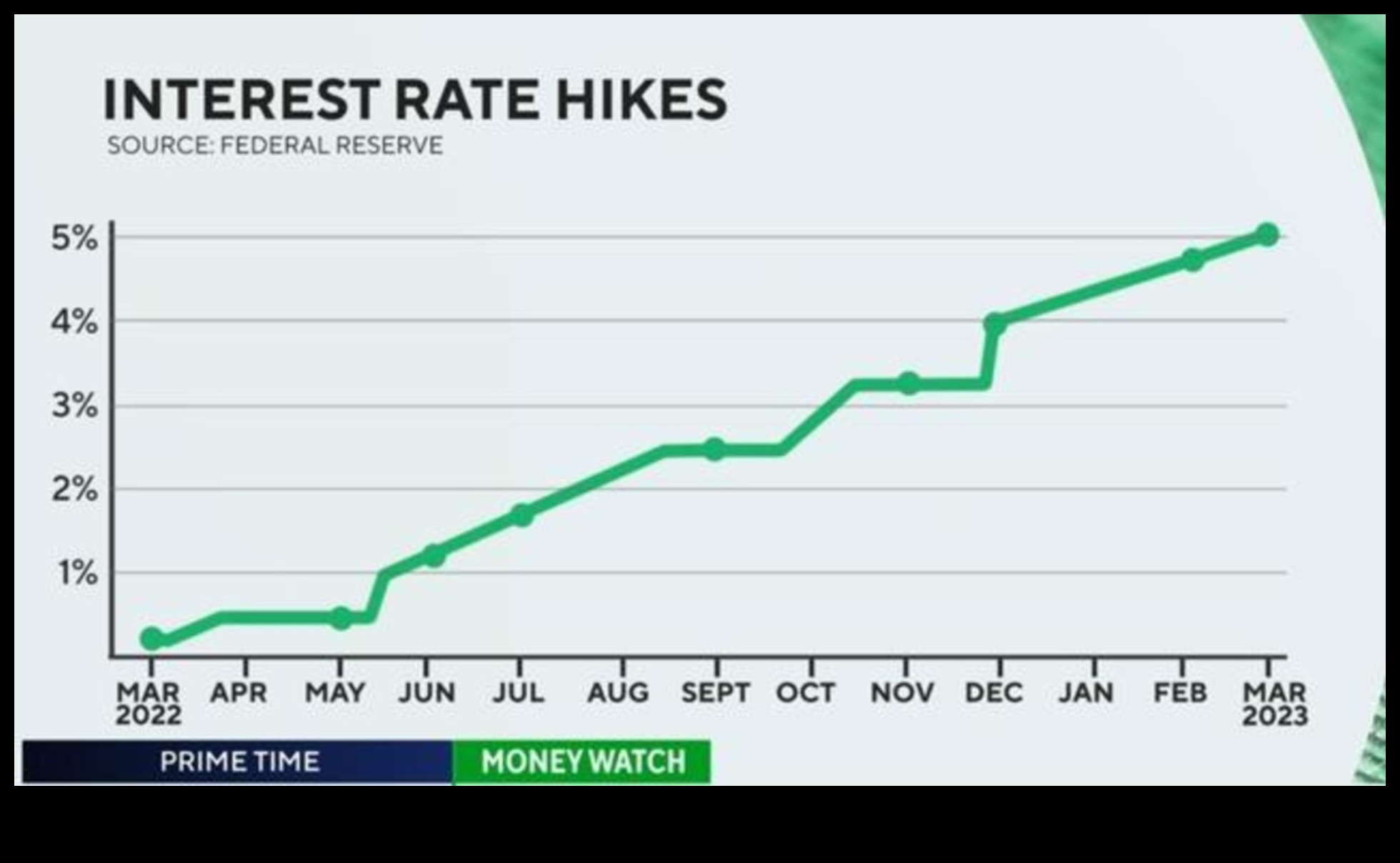
V. What are the effects of the federal funds rate on interest rates?
The federal funds rate is the benchmark interest rate for the U.S. economy. It is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can slow down economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can stimulate economic growth.
The federal funds rate also affects other interest rates in the economy. For example, when the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it typically causes other short-term interest rates to rise as well. This is because banks use the federal funds rate as a benchmark when setting their own lending rates. As a result, when the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for consumers to borrow money for things like mortgages, car loans, and credit cards. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for consumers to borrow money.
The federal funds rate also affects long-term interest rates, such as the yield on 10-year Treasury bonds. However, the relationship between the federal funds rate and long-term interest rates is not as direct as it is for short-term interest rates. This is because long-term interest rates are influenced by a number of factors other than the federal funds rate, such as inflation expectations and economic growth.
Overall, the federal funds rate is a powerful tool that the Fed can use to influence the economy. By raising or lowering the federal funds rate, the Fed can affect short-term interest rates, long-term interest rates, and economic growth.
VI. What are the effects of the federal funds rate on inflation?
The federal funds rate has a direct impact on inflation. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can slow down economic growth and lead to lower inflation. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money, which in turn makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money and invest. This can stimulate economic growth and lead to higher inflation.
VII. What are the effects of the federal funds rate on employment?
The federal funds rate can have a significant impact on employment. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to layoffs and slower economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to hiring and faster economic growth.
The relationship between the federal funds rate and employment is not always straightforward, however. For example, a study by the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco found that a 1% increase in the federal funds rate can lead to a 0.2% decrease in employment in the short run, but a 0.3% increase in employment in the long run.
The effects of the federal funds rate on employment are also influenced by other factors, such as the state of the economy, the strength of the labor market, and the policies of other central banks.
VIII. Effects of the federal funds rate on employment
The federal funds rate has a significant impact on employment. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which in turn makes it more expensive for them to hire workers. This can lead to job losses. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which in turn makes it cheaper for them to hire workers. This can lead to job creation.
The relationship between the federal funds rate and employment is not always straightforward. There are a number of other factors that can affect employment, such as the state of the economy, the level of demand for goods and services, and government policies. However, the federal funds rate is an important factor in determining the level of employment.
In general, a higher federal funds rate will lead to lower employment, while a lower federal funds rate will lead to higher employment. The following are some of the reasons why the federal funds rate has this effect on employment:
Higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money. This makes it more difficult for businesses to expand their operations and hire new workers.
Higher interest rates make it more expensive for consumers to borrow money. This makes it more difficult for consumers to purchase goods and services, which can lead to job losses in the manufacturing and retail sectors.
Higher interest rates can lead to a recession, which can cause job losses. A recession is a period of economic decline, during which businesses slow down or shut down and workers lose their jobs.
The federal funds rate is one of the tools that the Federal Reserve uses to manage the economy. By raising or lowering the federal funds rate, the Fed can influence the level of employment. When the Fed wants to stimulate the economy and create jobs, it lowers the federal funds rate. When the Fed wants to slow down the economy and reduce inflation, it raises the federal funds rate.
There are a number of challenges associated with using the federal funds rate to manage the economy. These include:
- The federal funds rate is a blunt instrument. It affects all businesses and consumers, regardless of their financial situation. This can make it difficult to target specific sectors of the economy.
- The federal funds rate can take a long time to have an effect on the economy. This is because it takes time for changes in the federal funds rate to be reflected in lending rates and other interest rates.
- The federal funds rate can be difficult to control. The Fed can only influence the federal funds rate by buying or selling Treasury securities. If the Fed buys Treasury securities, it increases the supply of money in the economy, which drives down interest rates. If the Fed sells Treasury securities, it decreases the supply of money in the economy, which drives up interest rates. However, the Fed cannot always control the demand for Treasury securities, which can make it difficult to achieve the desired effect on interest rates.
Despite these challenges, the federal funds rate remains an important tool for the Fed to manage the economy. By carefully considering the potential benefits and risks of using the federal funds rate, the Fed can help to promote economic growth and stability.
FAQ
Q: What is the federal funds rate?
A: The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans.
Q: How is the Federal Funds Rate set?
A: The Federal Funds Rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
Q: What is the target federal funds rate?
A: The target federal funds rate is the interest rate that the FOMC aims to achieve.