
What is the federal funds rate?
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is the primary tool that the Federal Reserve uses to control the money supply and influence the economy.
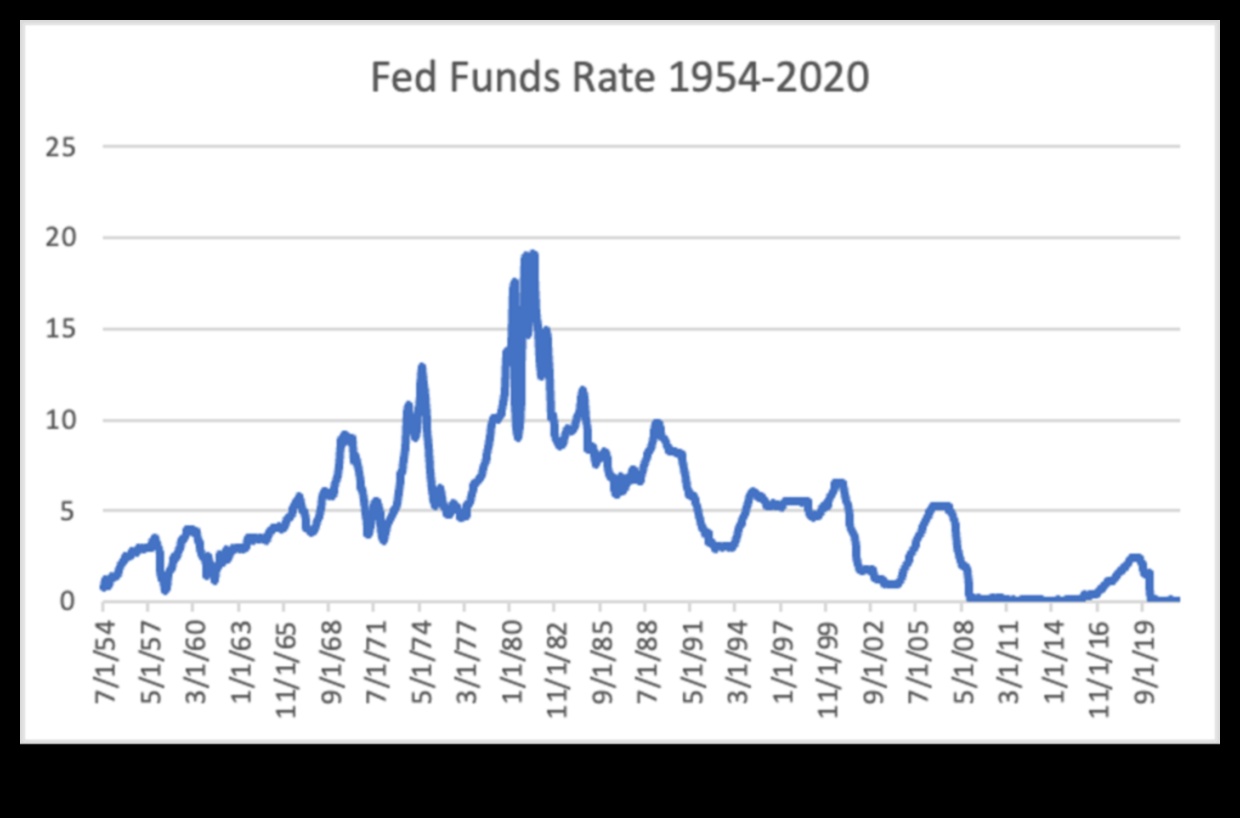
How is the federal funds rate set?
The federal funds rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is the monetary policy arm of the Federal Reserve. The FOMC meets eight times per year to set the federal funds rate. The committee’s goal is to keep the federal funds rate in a range that will promote economic growth and low inflation.
What are the effects of the federal funds rate?
The federal funds rate has a number of effects on the economy. It affects:
* The cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers
* The level of economic activity
* The inflation rate
* The value of the dollar
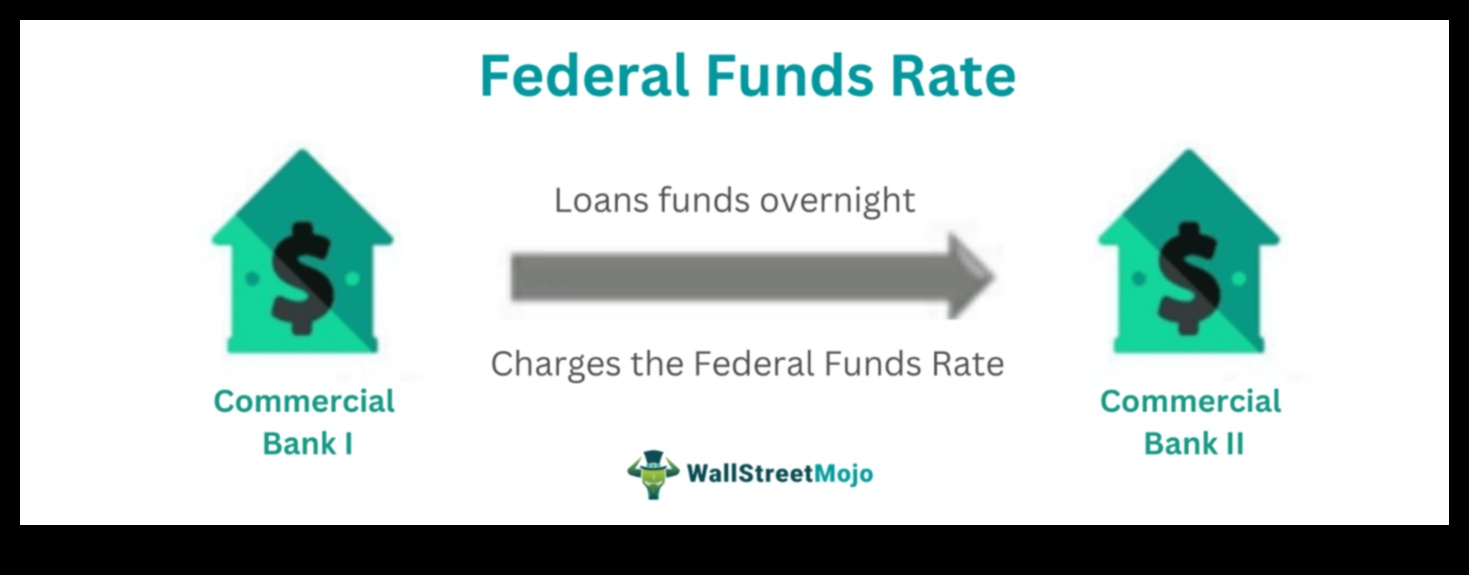
How does the federal funds rate affect the economy?
The federal funds rate affects the economy by influencing the cost of borrowing. When the federal funds rate is low, it is cheaper for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This can lead to increased economic activity, as businesses invest in new projects and consumers buy more goods and services. However, a low federal funds rate can also lead to higher inflation.
When the federal funds rate is high, it is more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This can lead to decreased economic activity, as businesses cut back on investment and consumers save more money. However, a high federal funds rate can help to control inflation.
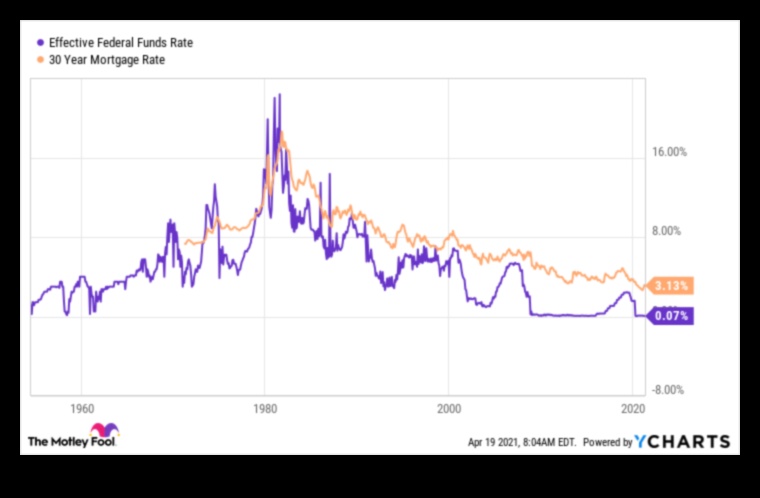
What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and inflation?
The federal funds rate and inflation are closely related. When the federal funds rate is low, it is more likely that inflation will increase. This is because a low federal funds rate makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to increased spending and economic growth. However, increased economic growth can also lead to higher demand for goods and services, which can push prices up.
When the federal funds rate is high, it is less likely that inflation will increase. This is because a high federal funds rate makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to decreased spending and economic growth. Decreased economic growth can lead to lower demand for goods and services, which can help to keep prices down.
What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and unemployment?
The federal funds rate and unemployment are also closely related. When the federal funds rate is low, it is more likely that unemployment will decrease. This is because a low federal funds rate makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to increased hiring. However, increased hiring can also lead to higher inflation.
When the federal funds rate is high, it is more likely that unemployment will increase. This is because a high federal funds rate makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to decreased hiring. Decreased hiring can lead to lower economic growth and higher unemployment.
What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and the stock market?
The federal funds rate and the stock market are also closely related. When the federal funds rate is low, it is more likely that the stock market will rise. This is because a low federal funds rate makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to increased investment and economic growth. Increased economic growth can lead to higher stock prices.
When the federal funds rate is high, it is more likely that the stock market will fall. This is because a high federal funds rate makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money, which can lead to decreased investment and economic growth. Decreased economic growth can lead to lower stock prices.
What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market?
The federal funds rate and the housing market are also closely related. When the federal funds rate is low, it is more likely that the housing market will boom. This is because a low federal funds rate makes it cheaper for people to borrow money to buy homes. However, a housing boom can also lead to higher inflation.
When the federal funds rate is high, it is more likely that the housing market will slow down. This is because a high federal funds rate makes it more expensive for people to borrow money to buy homes. A slowdown in the housing market can lead to lower inflation.
What are the challenges of using the federal funds rate to control the economy?
| Feature | Federal Funds Rate | Interest Rate | Monetary Policy | Federal Reserve | Central Bank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | The interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight | The cost of borrowing money | The actions taken by a central bank to influence the economy | The central bank of the United States | An institution that manages a country’s monetary policy |
| Role | To maintain the stability of the financial system | To encourage economic growth | To control inflation | To regulate banks | To issue currency |
| History | Established in 1913 | Has existed for centuries | Has existed for centuries | Established in 1913 | Has existed for centuries |
| Criticisms | Can be too volatile | Can be too high | Can be too low | Can be too independent | Can be too powerful |
II. How is the federal funds rate set?
The federal funds rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is the policymaking body of the Federal Reserve. The FOMC meets eight times per year to set the federal funds rate. The target federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. The FOMC uses a variety of factors to determine the target federal funds rate, including the inflation rate, the unemployment rate, and economic growth.
The FOMC can change the target federal funds rate by buying or selling Treasury securities. When the FOMC buys Treasury securities, it increases the supply of money in the economy, which lowers interest rates. When the FOMC sells Treasury securities, it decreases the supply of money in the economy, which raises interest rates.
The federal funds rate is an important tool that the Federal Reserve uses to control the economy. By raising or lowering the federal funds rate, the Fed can influence the cost of borrowing and spending, which can in turn affect economic growth, inflation, and unemployment.
II. How is the federal funds rate set?The federal funds rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is the monetary policy-making arm of the Federal Reserve. The FOMC meets eight times per year to set the federal funds rate. The target federal funds rate is the rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. The FOMC uses a variety of factors to determine the target federal funds rate, including inflation, economic growth, and unemployment.
II. How is the federal funds rate set?
The federal funds rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is the monetary policy-making body of the Federal Reserve. The FOMC meets eight times per year to set the federal funds rate. The target federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. The FOMC uses a variety of factors to determine the target federal funds rate, including the current economic conditions, inflation, and employment.
The FOMC can increase or decrease the target federal funds rate by buying or selling Treasury securities in the open market. When the FOMC buys Treasury securities, it increases the supply of money in the economy, which lowers interest rates. When the FOMC sells Treasury securities, it decreases the supply of money in the economy, which raises interest rates.
The federal funds rate is an important tool that the Fed uses to control the economy. By raising or lowering the federal funds rate, the Fed can influence the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers, which can in turn affect economic growth, inflation, and unemployment.
V. What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and inflation?
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is one of the most important tools that the Federal Reserve uses to control the economy. The Fed can raise or lower the federal funds rate in order to stimulate or slow down economic growth.
When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money. This, in turn, makes it more expensive for businesses to borrow money to invest in new projects or expand their operations. It also makes it more expensive for consumers to borrow money to buy a house or a car. As a result, economic growth slows down.
When the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money. This, in turn, makes it cheaper for businesses to borrow money to invest in new projects or expand their operations. It also makes it cheaper for consumers to borrow money to buy a house or a car. As a result, economic growth speeds up.
The relationship between the federal funds rate and inflation is complex. In general, a higher federal funds rate leads to lower inflation, and a lower federal funds rate leads to higher inflation. However, there are a number of factors that can affect the relationship between the two, including the state of the economy, the level of unemployment, and the actions of other central banks.
In the United States, the Fed has a dual mandate to promote maximum employment and price stability. This means that the Fed tries to keep the economy growing at a healthy pace while also keeping inflation under control. The Fed uses the federal funds rate as one of its tools to achieve these goals.
When the Fed judges that the economy is growing too fast and inflation is a risk, it will raise the federal funds rate. This will make it more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money, which will slow down economic growth and help to keep inflation in check.
When the Fed judges that the economy is growing too slowly and inflation is not a risk, it will lower the federal funds rate. This will make it cheaper for businesses and consumers to borrow money, which will stimulate economic growth and help to boost inflation.
The Fed’s decisions about the federal funds rate are closely watched by investors and businesses alike. The federal funds rate is a key indicator of the direction of the economy and the Fed’s monetary policy stance.
What is the federal funds rate?
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is the most important interest rate in the United States and is used by the Federal Reserve to control the money supply and the economy.
VII. What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market?
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is one of the most important tools that the Federal Reserve uses to control the economy. The Fed can raise or lower the federal funds rate in order to stimulate or slow down economic growth.
The federal funds rate has a direct impact on the housing market. When the federal funds rate is low, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money. This, in turn, makes it cheaper for people to borrow money to buy a home. As a result, the housing market tends to be more active when the federal funds rate is low.
Conversely, when the federal funds rate is high, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money. This, in turn, makes it more expensive for people to borrow money to buy a home. As a result, the housing market tends to be less active when the federal funds rate is high.
The relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market is not always straightforward. There are a number of other factors that can affect the housing market, such as the availability of housing, interest rates on mortgages, and economic conditions. However, the federal funds rate is a major factor that influences the housing market.
In recent years, the Federal Reserve has been raising the federal funds rate in an effort to slow down economic growth and reduce inflation. This has had a negative impact on the housing market, as it has made it more expensive for people to buy homes. As a result, the housing market has slowed down significantly in recent months.
It is important to note that the relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market is not permanent. The Fed can change the federal funds rate at any time, and this can have a significant impact on the housing market. As a result, it is important to keep an eye on the federal funds rate and its impact on the housing market.
What is the relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market?
The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is one of the most important tools that the Federal Reserve uses to control the economy. The Fed can raise or lower the federal funds rate in order to stimulate or slow down economic growth.
The housing market is closely linked to the federal funds rate. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it makes it more expensive for banks to borrow money. This, in turn, makes it more expensive for consumers to borrow money to buy a home. As a result, the housing market slows down.
Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, it makes it cheaper for banks to borrow money. This, in turn, makes it cheaper for consumers to borrow money to buy a home. As a result, the housing market picks up speed.
The relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market is not always direct. There are a number of other factors that can affect the housing market, such as the availability of housing inventory, consumer confidence, and interest rates on mortgages. However, the federal funds rate is one of the most important factors that influences the housing market.
Here is a table that shows how the federal funds rate has changed over time and how it has affected the housing market.
| Federal funds rate | Housing market |
|---|---|
| Low | Housing market picks up speed |
| High | Housing market slows down |
It is important to note that the relationship between the federal funds rate and the housing market is not always immediate. It can take some time for changes in the federal funds rate to have a noticeable impact on the housing market.
What are the challenges of using the federal funds rate to control the economy?
The federal funds rate is a powerful tool that can be used to influence the economy. However, there are also a number of challenges associated with using the federal funds rate to control the economy.
One challenge is that the federal funds rate is a blunt instrument. It affects all sectors of the economy, not just the one that policymakers are trying to target. This can lead to unintended consequences, such as slowing down economic growth or increasing unemployment.
Another challenge is that the federal funds rate is not always effective in achieving its desired effects. For example, if the economy is in a recession, the Fed may lower the federal funds rate in an effort to stimulate growth. However, if businesses are not confident about the future, they may not be willing to invest or hire new workers, even if the cost of borrowing is lower.
Finally, the federal funds rate is a reactive tool. It can be used to respond to changes in the economy, but it cannot be used to predict or prevent economic problems. This means that the Fed may need to take action to address an economic problem that could have been avoided if it had been anticipated.
Despite these challenges, the federal funds rate remains an important tool for monetary policy. It is a powerful tool that can be used to influence the economy, and it is one of the few tools that the Fed has at its disposal. However, it is important to be aware of the challenges associated with using the federal funds rate to control the economy.
FAQ
Q: What is the federal funds rate?
A: The federal funds rate is the interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. It is the primary tool that the Federal Reserve uses to control the money supply and the economy.
Q: How is the federal funds rate set?
A: The Federal Reserve sets the federal funds rate by changing the target range for the federal funds rate. The target range is the range of interest rates that the Fed believes is consistent with its economic goals.
Q: What are the effects of the federal funds rate?
A: The federal funds rate has a number of effects on the economy, including:
* It affects the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers.
* It affects the value of the dollar on the foreign exchange market.
* It affects the level of economic activity.
* It affects inflation.